(…continued from Part 3…)
***
Occupied Territories
The Zaporizhzhia Nuclear Power Plant (ZNPP) provided almost 25% of Ukraine’s electricity before the war. All six reactors were shut down, the last in 2023, because of the risks of operating it in a war zone. Russia plans to restart the ZNPP and connect it to the Russian power grid. In peacetime, it would take Ukraine two months to two years to safely restart the reactors. The two biggest requirements are a reliable water source to cool the reactors and a reliable energy source to operate the facility and circulate the water. Russia destroyed the Nova Kakhovka dam that created the Kakhovka reservoir that the ZNPP used to cool its reactors. Of the four high voltage lines that provided electricity to the ZNPP, two were destroyed by Russia and they could not rebuild them. The remaining two lines were shelled eight times, disrupting outside electricity and forcing the ZNPP to rely on backup generators. In 2022, the plant had fuel for 15 days of deisel generator operations. Additional generators have been brought to the site and removed over time. Here is a chronology of events.


***
Unknown Location
A Russian fiber optic drone moves behind a Ukrainian fiber optic drone. The rotors of the Russian drone cut the cable of the Ukrainian drone.
***
Baltic Sea
Beginning 1 July 2025, Sweden will check insurance documentation and improve other monitoring efforts of any ship passing through Swedish territorial waters or the economic zone. This will be applied to all ships but is directed at Russia’s shadow fleet ship in an effort to improve maritime safety and reduce environmental risks.
Two weeks ago, a sanctioned Russian ship was moving suspiciously around a 600-megawatt undersea cable between Poland and Sweden. After non-specific Polish military intervention, the ship sailed to a Russian port and a Polish naval survey ship headed to the site to observe the bottom of the sea.

A pair of Polish fighters intercepted a Russian Su-24 that was conducting dangerous maneuvers over the Baltic Sea. Russian aircraft frequently operate without activated transponders, without submitting flight plans and without maintaining radio contact with civilian air traffic controllers. In 2023, NATO conducted 300 intercepts of fighters and bombers. In 2024, most of the intercepts shifted from fighters and bombers to reconnaissance and transport aircraft as the fighters and bombers were supporting the war in Ukraine. In 2025, the interceptions continued.
There’s been a lot of events in the Baltic Sea, from interceptions of shadow fleet ships to verify documentation, legal status and safety, to Russian planes flying with their transponders off and violating airspace, to Russian detention of tankers. This article contains a long list of events.
***
Modern Warfare
A Major General (reserve) with 34 years of experience in serving with the Israel Defence Forces, maintains that no one fully understand the impact of the FPV drone outside of the Russian and Ukrainian armies.
• FPV-kamikadze (hereafter - just FPV) is not another new approach or weapon, it is a revolution in military business. The old doctrines no longer work.
• NATO generals have yet to realize the full depth of changes. The only ones who are improving in the FPV today are the armies of Ukraine and Russia.
• The FPV factor cannot be circumvented or ignored with accurate decisions (cost losses, for example), as it completely changes the very basis of the tactics.
• The phenomenal effectiveness of FPV is due to a combination of several factors: cheapness, fantastic accuracy and a range of tens of kilometers.
• FPVs provide a unique opportunity to concentrate the mass of fire damage (using FPV "herds") while maintaining decentralized forces.
• Separately it is necessary to mark FPV on fiber optic, which at this stage cannot be stopped, except by destroying the operator itself.
• FPV is unique in that the operator is in maximum (relatively the scale of the war) security, and it is extremely difficult to detect.
• Small drones and FPVs violated the main foundation of classic military thought - the concentration of effort and mass on specific areas. On a modern battlefield, you cannot deploy and concentrate more forces than your mouth.
• The defender can no longer rely on concentrated fortifications. The architecture of modern defense is a decentralized and deep web of positions, including a lot of false positions and deceptions.
• The attacker's tactics are also changing - this is a support to small tactical troops, which penetrate deep into the defender's orders, pulling out "arrows" (Ukrainians call it "pysunami").
• The offense is now based on the concentration of fire and means of defeat, rather than on the concentration of forces and maneuvers. This led to the attacker progressing extremely slowly as he relied on small troops.
• Any advanced logistics centers or headquarters turn into death traps due to their cloutness.
• The solution for logistics is decentralization, and for command it is underground care and support for wired and satellite communication.
• The revolutionary change is the change of the very architecture of the frontline - now it is a 40-kilometer "crater of death", where being in open space for at least 15 minutes will result in inevitable death.
• A skillful combination of forces in all-round military combat — air, artillery, and mass FPV together with ground forces — can result in tactical success.
• Air superiority now also needs to be shared. Since this very superiority has little impact on the space of the "crater of death" 40 km at the front, - the so-called new space of small aviation.
• The day when we will see the launch of full-fledged swarms of drones with fiber optic and controlled combat AI is near. This will result in the unnecessary number of operators.
• This situation raises the question of a person’s position regarding the “man-machine” spike on the forthcoming battlefield.
• Both specialists emphasize that the AOI should literally make a leap in this area and deploy FPV drones in all army units. All bureaucratic constraints hindering this are also required to be broken.
• Carelessness and ignoring this technology will lead to paying double the price. We are talking about revolutionary technology, not a local phenomenon.
Schemes: the first is a battlefield and a threat; FPV is unique by its fantastic cheapness and mass. The second is the area of 40 km, the so-called "Crater of Death", where staying open for 15 minutes will result in your death.
***
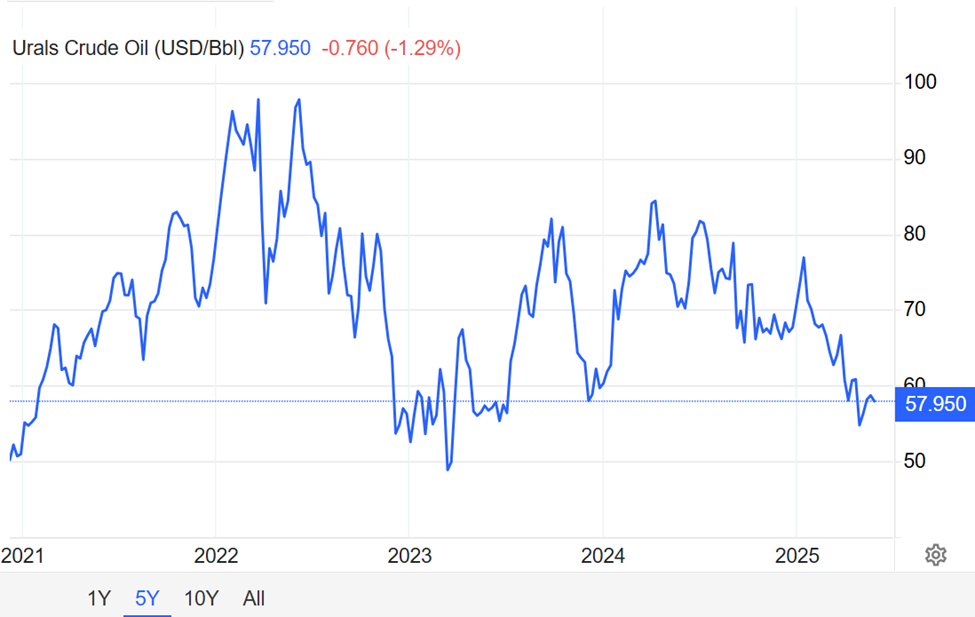
Russia
In recent years, the 22 nations of OPEC+ agreed to gradually reduce production to increase the price of oil. Some members of the group, notably Kazakhstan, exceeded their agreed upon production quotas, benefiting from higher prices as other states lowered their production. Saudi Arabia and selected OPEC nations decided to increase production by 411,000 barrels a day in May, then June and now July to recapture market share and punish Kazakhstan. Russia is part of the so-called “Voluntary Eight” OPEC+ members that are increasing their production. Despite producing more oil, Russia is making less money.
The Russian naval base at Severomorsk on the Kola Peninsula was hit by drones. Among other ships, nuclear subs are based there. Details are scares other than smoke and detonating ordnance.
The NPO Splav facility in Tula that produces MLRS systems, guided and unguided missiles was attacked by a drone again.
The Murom Instrument-Making Plant was attacked on April 30 and a warehouse for ignition caps was destroyed. On May 27, 11 drones reportedly attacked it again and three were shot down. The damage was not reported.
Drones attacked the Alabuga drone plant again despite local air defense systems.
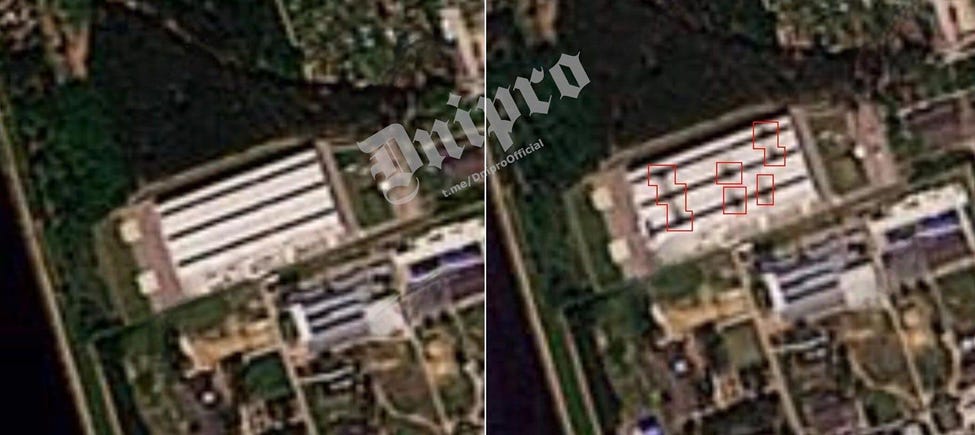

At least eight drones hit a drone factory in the Moscow region. The attack started a fire.
A warehouse in a Kamensky Combine chemical plant was hit by two drones.
A technology park that has 150 companies producing electronic equipment, manufacturing control and measuring instruments, and optical devices was attacked. A building was damaged.
Last week, at the Avangard plant in St. Petersburg, explosions were heard before a fire broke out on the upper floors of the facility. It produces radars for the S-400 and Tor systems. In April and August of 2024, fires broke out at the Avangard plant in Sterlitamak, 800 km from Ukraine. This plant builds components for rocket systems.
Russia is modernizing it nuclear missile silos sites in the Orenburg region with the construction of fencing, concrete buildings with blast-resistant windows and doors, underground tunnels and motion, seismic and radiation sensors. Much construction materials came from the west, with the German firm Knauf providing the most.
Russia outlawed voluntary surrender in September 2022 with a sentence of 3 to 10 years. With the exchange of 1000 prisoners, some Russian bloggers are calling for interrogation of freed prisoners saying most of them should have killed themselves rather than face Ukrainian torture and interrogation, which would provide information that would put their fellow soldiers at risk.
***
Ukraine
On the night of June 1st, Russia sent 472 drones (some as decoys, others armed with warheads), three ballistic missiles and four cruise missiles. Ukraine says 385 threats were neutralized and said 18 locations were struck.
Another missile strike hit a Ukrainian training center, this time in the Dnipropetrovsk Oblast. After the air raid siren sounded, most were in bunkers, but at least 12 were killed and 60 were wounded. An investigation is under way but the commander of the ground forces, BG Drapatyi, offered his resignation for not pushing enough to convince officers to change their attitudes towards the troops. He believes that an army without accountability for its leaders cannot function and decided to lead by example and take responsibility. There is no word on whether his resignation was accepted.
Last November, Ukraine set a goal of producing 3,000 cruise and drone missiles in 2025. They are now establishing separate funding for the program to accelerate production.
Ukraine established a components library that vets Ukrainian companies and allows them to offer their components to other Ukrainian companies that build weapon systems. Along with foreign funding of Ukrainian weapons production, this is an effort to grow Ukraine’s defense industry and reduce reliance on foreign production. The library has 156 users and a list of 97 components in the categories of antennas, amplifiers, and electronic warfare generators, maintenance services, battery assemblies, flight controllers, frames, propellers, FPV engines, and other related peripherals, such as drop systems, servo rails, video amplifiers, and combat unit components.
A parallel initiative seeks to fully integrate Ukraine into the European defense industries. Ukraine can already take part in any EU initiatives on an equal footing with other EU manufacturers.
About 50,000 Ukrainians have lost a limb in combat. A third will go back to the jobs they had before the war. A third will do something new. And another third will return to combat.
***
(…to be concluded in the Part 5…)




It seems that everyone is literally "blinded" by current drone technology development. We tend to forget that drones are extremely soft targets. They can be easily fought by even cheaper means then they are. Amors and speed crafts appeared for a reason in the past.
With fully implementing existing anti drone technology, drone swarms, while could become a norm, would not be so dreaded.
And also with relative simplicity of organising armor protection, people would get back inside those. And then after a turn of spiral "normal" doctrine would be back, though significantly extended and updated with requirements of the time.
The most significant change though, needs to come in a multisensor recon. Where litteraly one would not be able to hide any aspect of military activity 100-150 km deep from the frontline. And then whoever wins that "middle sky" wins the whole battle, because of being able to interdict logistics 100 km deep.
So I suspect we might see a few changes of approach, and technology leaps before this war is over.
Some (likely not full) "errata" for the auto-translation of Yigal Levin's post:
"you cannot deploy and concentrate more forces than your mouth."
- more forces than a company (rota)
"pulling out "arrows" (Ukrainians call it "pysunami")."
- You can maybe translate this as "pricks" (as in "Pudding is a ***", but a more "cute/childish" version). :) And if anyone cares, the word ending in "ami" is objective case from "pisiun" (sing.) & "pisiuny" (pl.).
"and for command it is underground care and support for wired and satellite communication"
- moving underground and relying on [wired/sat comms]
"all-round military combat"
- combined arms (= общевойсковой бой)
"and controlled combat AI"
- controlled BY combat AI
"this will result in the unnecessary number of operators."
- result in not needing many operators
"“man-machine” spike"
- "man-machine" joint/seam/combination etc