(….continued from Part 4…)
Our experience is showing that you, dear reader, particularly appreciate our discussions of the ‘equipment’ - and explanations how ‘things making bang work’. Indeed: ‘how is the warfare working’. Thus, we’ve decided to expand our coverage of such topics. For this round of his weekly round-up, Don was so kind to prepare a ‘bigger than usual’ section covering Equipment. This is going to be the first part: the second is to follow in the Part 6.
***
Equipment
Beating predictions, Romania will donate a Patriot system to Ukraine. It bought seven systems and has received four of them, two of which are operational. Part of the deal was an agreement that the US and western allies would provide Romania with an equivalent system to help defend their skies. On a couple of occasions, Romania has been hit by debris from Russian attacks on the Ukrainian side of the border…https://www.kyivpost.com/post/34612
Switzerland bought 80 PAC-3 Patriot missiles but for the next 16 months the US will send them to Ukraine instead. Part of the contract allowed the US to delay delivery in case of an extraordinary event that impacts US security, and the US invoked Russia's attack in Ukraine to divert Patriot production to Ukraine. (Patriot deliveries to Israel and Taiwan will still continue). At the same time, Switzerland will now allow their weapons and the weapons they sold others to be sent to Ukraine. Earlier in the war they wouldn’t let Germany send Swiss-manufactured ammo to the Gerpards in Ukraine. A NATO official said Switzerland could be neutral, or they could sell arms to NATO, but they couldn’t be both. After long philosophical questions of morality and the greater good, and after seeing their military exports fall 27%, they reversed their position…https://x.com/blyskavka_ua/status/1803530237625704508
Rheinmetall received an €8.5 billion order, the largest in its history, for 155 mm shells. Delivery will begin in 2025. Germany will receive most of the shells and will send some to Ukraine. The Netherlands, Estonia and Denmark will also receive shells to replenish their stockpiles…https://www.rheinmetall.com/de/media/news-watch/news/2024/06/2024-06-20-rheinmetall-erhaelt-rekordauftrag-ueber-155mm-munition
Because of Ukraine’s strong technological base, new legislation, and $2 billion in US aid for technology, Ukraine approved 700 drone inventions, 40 of which are being used on the front lines, and 100 Ukrainian companies develop and produce drones. Their production rate increased by a factor of 100, meaning they don’t have to buy as many drones. This means their supply of drones is more secure, especially since many of them were bought in China. In fact, 90% of the drones Ukraine uses now are produced in Ukraine…https://kyivindependent.com/opinion-ukraine-is-racing-to-ramp-up-domestic-defense-production/
Ukraine will receive 547 AIM-120D3 and AIM-120C8 missiles in the next year…https://x.com/ColbyBadhwar/status/1803828405575545013
Using technology it created for NASAMS, Norway built the National Maneuver Air Defense System (NOMADS), a short-ranged air defense system. The system can be mounted on a variety of chassis but the baseline vehicle will be the German Armored Combat Support Vehicle (ACSV) G5. While NASAMS is a static system, NOMADS is designed to accompany ground troops. It has an AESA radar with a 31 km range, laser range finder, a day/night camera and a thermal camera. It has the same command and control architecture as NASAMS, NATO-standard IFF, UHF and VHF communications. The standard missiles are four AIM-9X Block 2 Sidewinders with a 35 km range, and also a .50 cal machine gun and an optional radio frequency directional jammer to provide some level of protection against FPV drones. The Norwegian Army will use the Iris-T SLS missile with a 12 km range. Germany is considering buying some of these vehicles for Ukraine…https://www.twz.com/land/norways-nomads-short-range-air-defense-system-unveiled
Russian visually confirmed BTR losses are over 1000 and BMP losses are over 3000.
Just to provide a timeline on modern tank peacetime production, Germany is ordering 105 Leopard 2A8 tanks. Those 105 tanks will be delivered in 2030…https://x.com/HoansSolo/status/1803778377280631231
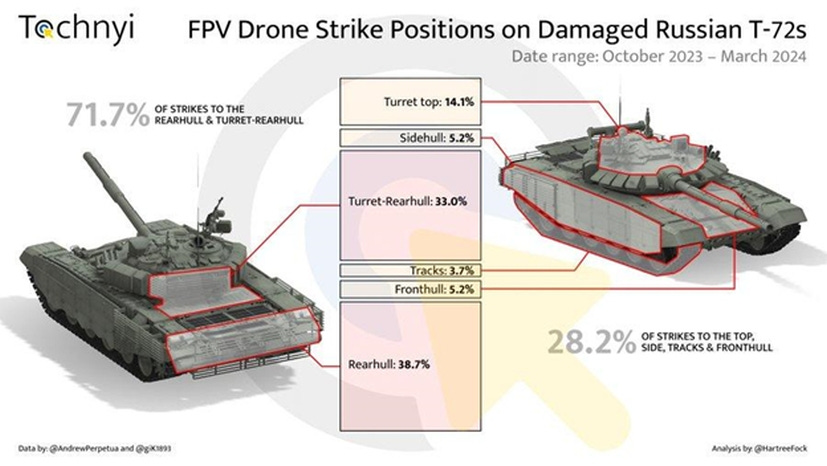
An extensive thread focusing on Russian tank losses from drones from September, 2023 to March, 2024…https://x.com/HartreeFock/status/1803873681396920689
Electronic Warfare is very dynamic and ever evolving. This is the current impact of Russian jamming on Ukrainian weapons.
● Commercial Off The Shelf (COTS) drones are the most widely used drones and the most affected by jamming. Ukraine adjusts by monitoring the frequencies that are being jammed and then changes their software and antenna to utilize different frequencies. Technicians are also working to make drones more resistant to jamming and still remain inexpensive. A year ago, Ukraine was losing 10,000 drones a month to jamming. I haven’t seen current numbers of jamming losses but it’s a lot less than 10,000 a month. It was reported that Ukraine also fielded a drone that is using AI terminal guidance which does not rely on operator commands, rendering jamming ineffective.
● Ukraine was given around 7000 Excalibur 155 mm shells. They were effective 70% of the time. Once the shell was jammed and cut off from the GPS it had to rely on its inertial guidance and the success rate dropped to 6%. Due to the small supply of shells and the accuracy issues, Ukraine largely stopped using the $68,000 shell.
● The GMLRS rockets fired by HIMARS and MLRS have been affected by jamming but Ukraine adjusted. EW resistant reconnaissance drones that seek targets can determine the EW environment. If the GPS frequencies aren’t being effectively jammed then GMLRS can be fired there. If it is being jammed, then Ukraine will sometimes run Suppression of Enemy Air Defenses (SEAD) missions in which Ukrainian aircraft will fire HARMs missiles that home on the jammer. HARMs has a 150 km range but these are still dangerous missions for Ukrainian aircraft. Once the jammer is destroyed, or once the radar is turned off and moved (suppressed), the GMLRS can be fired. Another alternative is to fire multiple rockets at the target, increasing the odds that the internal guidance system will be accurate on one of the missiles. In any case, there has been a steady stream of videos showing effective GMLRS strikes, indicating it is still very effective in an EW environment.
● JDAM-ER bombs also use GPS and are not immune to jamming but they are on target 60% of the time. There are plenty of videos in which four bombs hit the same building. Reconnaissance drones and SEAD missions can also play a supporting role in JDAM missions. JDAM’s are equipped with anti-spoofing devices so it can only be jammed, not be fed false data. On top of that, the US ordered Home-On-Jam seekers for JDAM. This means that the same jammers that are targeting JDAM bombs will then be targeted by the bombs. The JDAM-ER (Extended Range) has a 45 km range and the Russian Zhitel has a jamming range of about 30 km. It is possible that the JDAM could be aimed at a target, then a jammer could interfere with the GPS signal and the algorithm could steer the bomb to the source of the jamming if it is within range. The order for these seekers will be completed by October 1, 2025.
● Ground Launched Small Diameter Bombs (GLSDB) are fired from HIMARS/MLRS and they haven’t worked. One reason is because the booster rocket has separation issues. The other reason is jamming. They have solutions for both issues but it will take months to implement and test.
● Small Diameter Bombs that are dropped by aircraft are 90% effective. Since the EW environment is always changing, it’s possible that it can change in the future.
(….to be continued…)






Btw 1st shipment of shells secured by CZ initiative is at UA as confirmed our PM Petr Fiala👍
Hope more and more will follow soon as "participating" countries will change promisses into real money
Very interesting. Thanks Dom 👍